November 12, 2025
November 12, 2025
Understanding Thyroid Disorders – Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
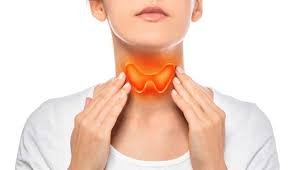
The thyroid gland may be small, but it plays a powerful role in regulating the body’s metabolism, energy, and hormone balance. When this butterfly-shaped gland located at the front of your neck doesn’......